

Port Forwarding Using AWS System Manager Session Manager

Written By Saugat Tiwari
Jan 18, 2024
Saugat Tiwari is a results-driven DevOps Engineer specializing in AWS cloud infrastructure, automation, and security, with a proven track record of implementing efficient CI/CD pipelines and optimizing cloud-native solutions while maintaining robust security practices.
Latest Blogs

DevOps Consulting Services and Solutions for U.S. Companies (2025)
U.S. companies face growing pressure to ship software faster, modernize legacy systems, and make eve...

Adex International
Jun 30, 2025
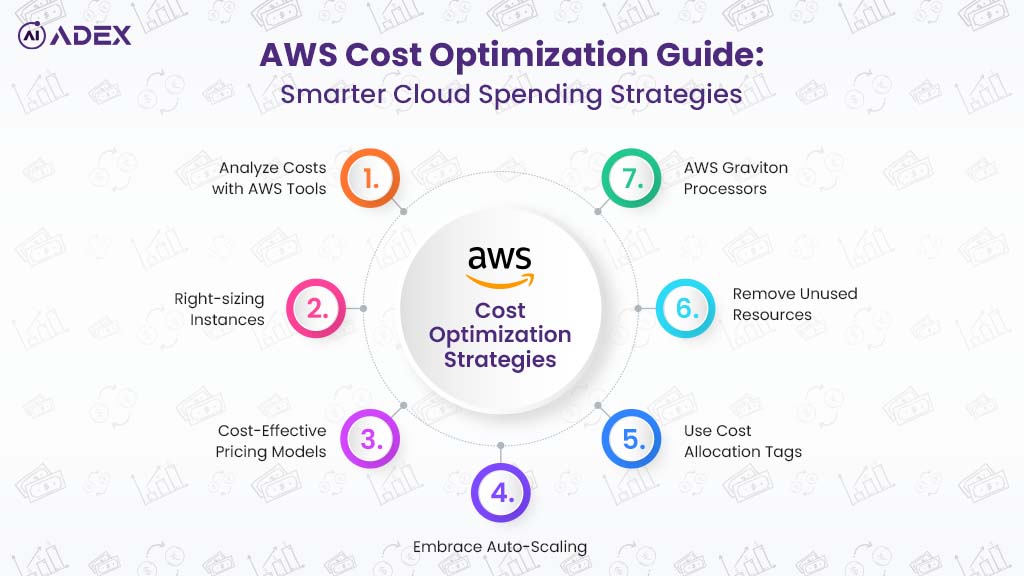
AWS Cost Optimization Guide: Smarter Cloud Spending Strategies
Amazon Web Services (AWS) powers millions of businesses worldwide with flexible, scalable cloud infr...

Prashansa Joshi
Jun 25, 2025

How to Submit an AWS Consent to Assignment Request
When transferring an AWS account between two legally distinct entities, such as during a merger, acq...

Adex International
Jun 24, 2025

A Complete Guide to Your Managed IT Service
A well-structured Managed IT Service Contract is more than a legal technicality; it is a strategic d...

Adex International
Jun 18, 2025

How to Deploy Globally Available GenAI APIs Using AWS Global Accelerator and Bedrock
GenAI APIs enable real-time capabilities across various workloads, including intelligent assist...

Papila Ghising
Jun 18, 2025

How to Deploy n8n on AWS EC2 Using Docker
Many automation platforms that rely on fully-managed hosting come with trade-offs: costly pricing ti...

Chandra Rana
Jun 13, 2025

How Agile and DevOps Complement Each Other: Best Practices for Joint Implementation
Agile and DevOps are often seen as distinct methodologies—Agile focuses on flexible planning, collab...

Adex International
Jun 11, 2025

Building a Serverless Stock Market Data API with Caching, Lambda, and DynamoDB
Delivering real-time stock market data efficiently to millions of concurrent users is a significant...

Adex International
Jun 06, 2025

Recent Development In AWS: May 2025
With innovative updates every month, AWS continues to empower cloud users, and the May 2025 releases...

Chandra Rana
Jun 03, 2025

IT Infrastructure Outsourcing Services Explained: Benefits and Best Practices
Delegating IT infrastructure to external providers has become a strategic decision for companies see...

Adex International
Jun 02, 2025