

Migrate Gitlab PostgreSQL Database to Custom Location Using Ansible

Written By Adex International
Jan 18, 2024
Adex is a Cloud Consulting company providing a wide array of end-to-end services - from consulting to managed services. As a Multi Cloud Solution provider with a customer-first approach, we enable enterprises to build, optimize cloud and drive tangible business outcomes.
Latest Blogs
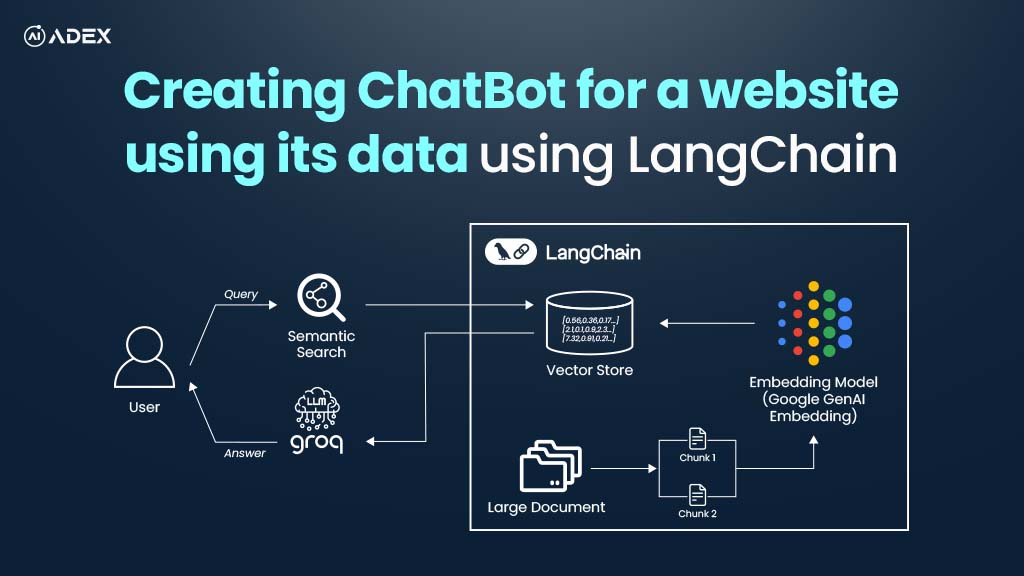
Creating Chatbot For Website with LangChain and Groq
Chatbots are transforming the way users interact with websites and services, helping them navigate c...

Adex International
Aug 21, 2025

Top DevSecOps Practices to Secure Your Cloud Environment
Cloud pipelines evolve rapidly, but every new feature can introduce hidden security risks stemming f...

Chandra Rana
Aug 18, 2025
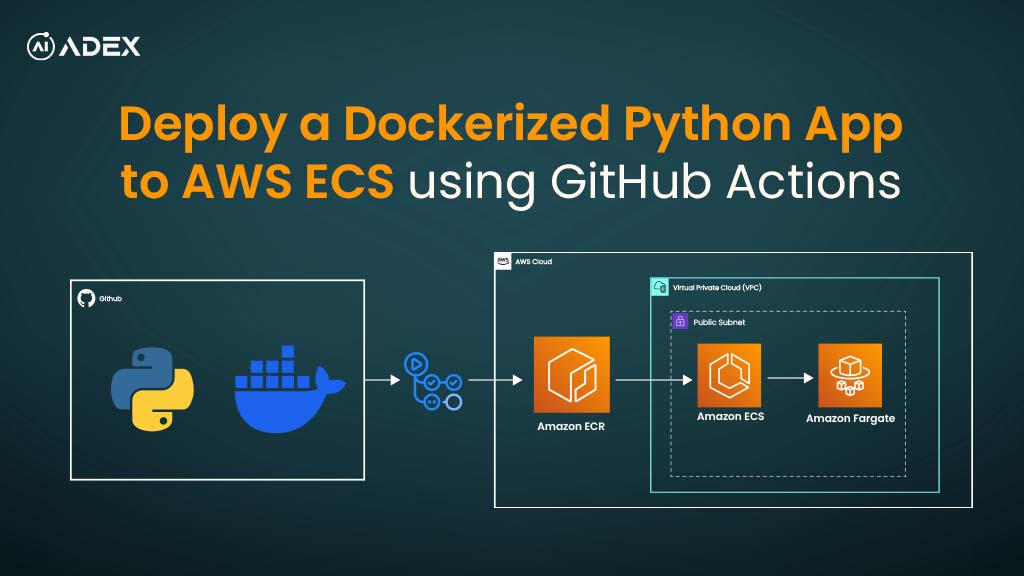
Deploy a Dockerized Python App to AWS ECS Using GitHub Actions
Deploying applications to the cloud reliably can be challenging due to inconsistent environments, sc...

Chandra Rana
Aug 13, 2025
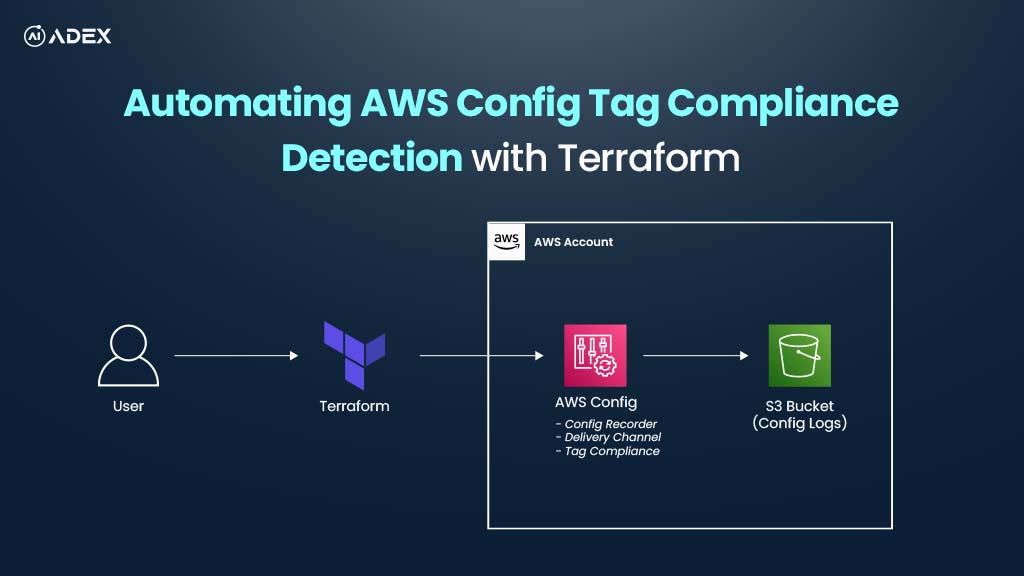
How To Automate AWS Resource Tag Compliance Checks with AWS Config and Terraform
Consistent tagging of AWS resources is vital for governance, cost management, security audits, and o...

Sneha Tuladhar
Aug 08, 2025

AWS Monthly Updates – July 2025: GenAI, Free Tier Boost, and Deployment Enhancements
Redefining what’s possible in the cloud, AWS rolled out its July 2025 updates aimed at accelerating...

Chandra Rana
Aug 05, 2025

Steps to Purchase AWS Reserved Instances: Cut EC2 Costs with Confidence
Did you know businesses can save up to 72% on EC2 costs simply by choosing the right pricing model?...

Prashansa Joshi
Jul 31, 2025

Generative AI Consulting Services: Launch Your Business to New Heights with AI
The pace of business transformation has never been faster, and customer expectations are shifting by...

Adex International
Jul 31, 2025

AI & ML Services for Modern Businesses: Benefits, Service Categories and Partner Evaluation
AI and ML are no longer emerging trends; rather, they are transformative capabilities driving busine...

Adex International
Jul 30, 2025

Offshore Development Centers: Your Guide to Success
Offshore Development Centers (ODCs) are increasingly viewed as a strategic and effective means for f...

Adex International
Jul 29, 2025

Purchasing AWS Savings Plans (1 or 3 year): Step-by-Step Guide for Cloud Cost Optimization
Managing AWS costs has become a top priority as cloud spending continues to outpace other IT expense...

Prashansa Joshi
Jul 21, 2025